Option master has appeared in the Protrader terminal
Hey there, Protraders!
The new option module called “Option master” has appeared in the Protrader terminal; it allows estimating option positions, plotting option profiles, modelling their change depending on different market factors, and holding testing of the real option positions “on paper”.
For a start, let’s get acquainted with the concept of options. Derivative financial instruments have long been used by market participants to achieve their goals. Also, these instruments called “derivatives”. Derivative is a contract by which the parties who enter into it undertake an obligation or get a right to perform some actions in relation to the underlier. Stocks, commodities, currencies, or other derivative instruments etc. can be an underlier. Due to its specific properties derivatives are widely used by traders worldwide. Today we’ll discuss the options. Option – is a contract that gives the right, but not the obligation, to option contract holder to buy or sell the underlier in the future at a predetermined price for a predetermined length of time. Seller of the option, i.e. the person who has issued the option should become the counterparty in the case of option realization. Thus, using the options, trader can make a deal in relation to the future price of the underlier. This fact makes them an attractive tool to limit losses or hedge the risks associated with the activities on the financial markets. Options are divided into two types:
- Put option – gives a right to sell the underlier;
- Call option – gives a right to buy the underlier.
Let’s consider a small example. If the underlier price is 100 conventional units and market participant faces with task to buy this asset at a price not more than 120 conventional units, it can act in two ways:
- Buy directly the underlier.
- Not waiting for the underlier growth, buy Call option with the strike price 120.
In case if the underlier price is higher than selected level 120 by the option expiration date then buyer of the option can realize his right to buy asset, and the option will turn into a long position by the underlier with open trade price = 120. The same mechanics acts for sale of the underlier and Put options. At the conclusion of the option trade, the option buyer pays premium to the option seller. The fact that the option for buyer is not the obligation, but the right to buy/sell the underlier, gives a possibility to create protective (hedging) strategies when trading on financial markets.
Example: the wheat grower calculated the cost of his future crop – $ 700 per bushel taking into account the funds that he deposited. If due to any factor during the crop realization, the wheat price will be lower than calculated price, the grower will incur a loss. In this case, the wheat grower can buy Put option by his calculated price. Let Put option with strike price of $ 700 cost $ 20. Let’s consider the possible variants of event development. If the wheat price during the crop realization is at the level of $ 600, then the grower uses his right to sell wheat at the price of $ 700 and his loss will be only $ 20 (premium paid for buying the option). If the grower didn’t use the options, then his loss would be $ 100. But probability of the underlier price growth to values higher than calculated also exists. Let the wheat price at the moment of crop realization will be $ 800, and then grower won’t use his right to sell the wheat at the price of $ 700, and will sell his product at the market price, earning additional profit. Thus, the wheat grower using Put option limits his market risks when realizing the crop.
Options are widely used not only by physical hedgers, but also by ordinary speculative traders. Option contracts can be sold/bought as a separate asset.
Classification
Let’s consider classification of the options:
Options are divided into series by time before contract expiration. Timeframes of the series are determined by the exchange.
Options are divided into two main groups by the execution type:
- American option. It can be executed at any time of option’s life.
- European option. It can be executed only after expiration date of the option contract.
By the state relatively to the underlier price options are divided into:
- Options called “out of the money” (OTM). State of the option when the underlier price is higher than strike price for Put options or lower than strike price for Call options;
- Options called “at the money” (ATM). State of the option when the underlier price fluctuates near the option strike.
- Options called “in the money” (ITM). State of the option when the underlier price is higher than strike price for Call options or lower than strike price for Put options.
Price formation
We’ve got acquainted with the basic concepts of the option trading.Let’s move to the price formation.
Price formation of the options is nonlinear and depends not only on the underlier price, but also on the period prior to the option expiration date, risk-free rate by the underlier and the implied volatility. Generally accepted calculation model of the theoretical option price is the Black-Scholes model.
To describe the dependence of the option price from the written above values so-called "Greeks" are used. These are the derivative values with the names of some symbols of the Greek alphabet.
“Greeks”
- Delta – characterizes the sensitivity of the option price to the change of the underlier price. Shows, how the option price will be changed if the underlier price changes on 1 point. Mathematically, this is the first derivative of the option price by the underlier price.
- Gamma – characterizes the speed of the option delta change when changing the underlier price. It shows how the option delta will be changed if the underlier price changes on 1 point. Mathematically, this is the second derivative of the option price by the underlier price.
- Theta – characterizes the speed of the option price change depending on the time remaining to expiration of the option contract. Sometimes, this coefficient is called as the rate of time decay. Theta has low values for the options with distant expiration date, and increases with decreasing of the term till expiration.
- Vega – characterizes the sensitivity of the option price to the change of the implied volatility. Shows how option price will be changed if the volatility changes on 1%. Mathematically, this is the first derivative of the option price by volatility.
- Rho – characterizes the sensitivity of the option price to the change of the risk-free rate.
Using “Greeks”, we can estimate the sensitivity of the option position to any of the option price formation factors, and thus to identify its strengths and weaknesses. And also estimate the risks.
The most difficult to understand from the option price formation factors is the implied volatility. Its impact on the option price formation is very large. But what is it? How does measure this parameter?
Volatility – is the measure of the underlier price variability.
Implied volatility – is the assessment of the future underlier volatility which is set by option market participants by means of options trading. It means that from the price of any option by Black-Scholes model we can get the value of the future volatility which is forecasted by the option market participants. Change in implied volatility affects the “Greeks” and directly the option price.
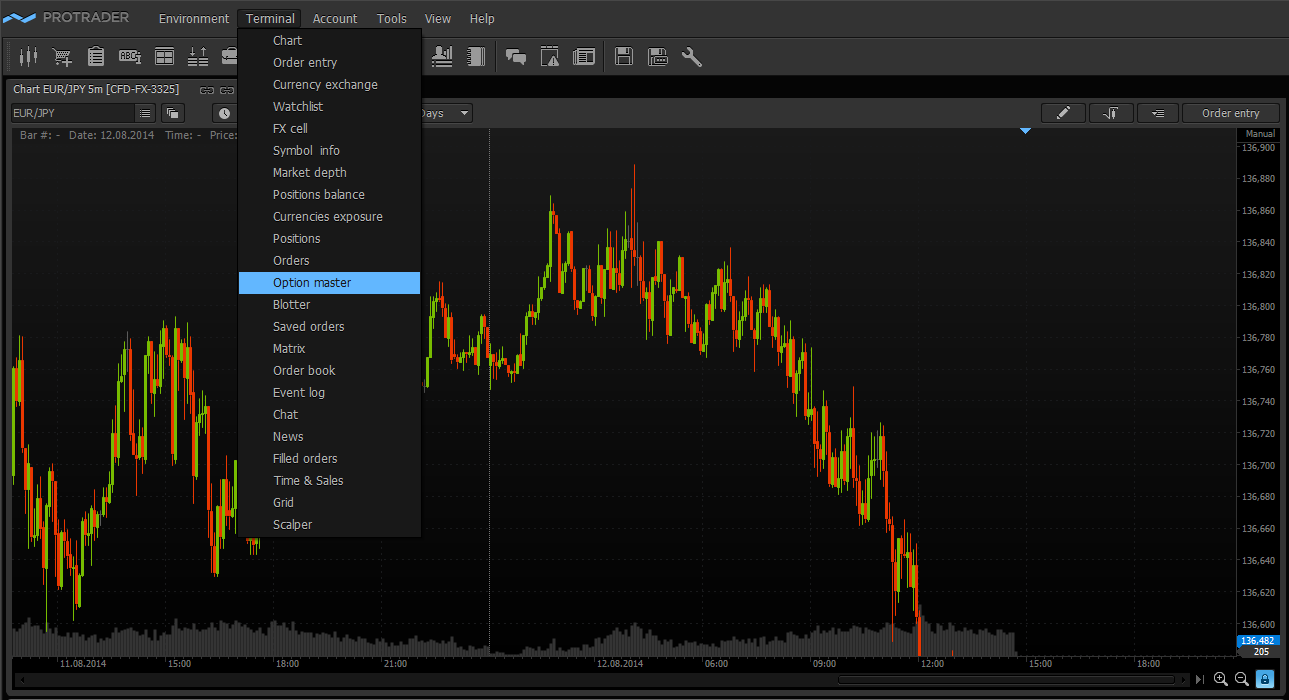
For the traders who uses the options in their trading is very important to understand the price change degree of their option positions depending on the changes of market factors. To provide this, the so-called option profiles are used, by which we can determine a theoretical option price by the set parameters. But often, program products which build such profiles don’t have functions for testing the options in the change mode of implied volatility. That carries a serious error in the assessment of market risks. The “Option master” module of the Protrader terminal offers wide functionality for the option strategies’ assessment. Using “Option master” the traders can estimate risks of their option positions when changing all possible market factors, thus prepare themselves to the most unfavorable market situation. This gives a possibility to design the schemes out of these situations with minimal risks. Also, this module allows testing “on paper” the most interesting option strategies and viewing their real market dynamics.
To run “Option master” you need to choose the corresponding item in the “Terminal” menu.
In the next article we will consider in details the “Option master” functionality and its use in the option trading.
Have not tried PTMC yet? There is no better way to boost knowledge than to use it! Start trading with PTMC now!